In a fast-paced world where time is a luxury, the quest for effective and efficient workout regimens has never been more paramount. Enter High-Intensity Interval Training (HIIT workout), a fitness revolution that has taken the exercise world by storm. With its unique blend of intense bursts of activity followed by short recovery periods, HIIT offers a time-efficient and highly effective approach to achieving fitness goals. This article delves into the science, benefits, techniques, and precautions associated with HIIT, shedding light on why it has become a go-to workout for individuals seeking maximum results in minimal time.
Table of Contents
what is hiit workout
HIGH-INTENSITY INTERVAL TRAINING is the clock-centric protocol that allows you to pack a ton of focused exercise attention into a short amount of time. You might know it better by the shorthand term used by fitness coaches and group training acolytes everywhere: HIIT workout.
The main appeal of HIIT for many people is that it’s an incredibly versatile format that allows for condensed training times. “A lot of people are super busy, and can’t allot an hour in the gym. You don’t need close to an hour for an effective HIIT session; even 20 to 30 minutes of focused work can be more than enough for the most well-conditioned exercisers.
The Science Behind HIIT workout

The science behind High-Intensity Interval Training (HIIT) revolves around the physiological responses that occur in the body during and after high-intensity exercise. HIIT is designed to push the body into an anaerobic state, where oxygen demand exceeds oxygen supply, resulting in a cascade of metabolic and cardiovascular adaptations. Let’s delve into the key scientific aspects that underpin the effectiveness of HIIT:
- Anaerobic Metabolism
- Elevated Heart Rate
- Excess Post-Exercise Oxygen Consumptio
- Elevation of Growth Hormones
- Mitochondrial Biogenesis
- Enhanced VO2 Max
Anaerobic Metabolism
During intense physical activity, the body’s demand for oxygen surpasses its ability to supply oxygen to the working muscles. This leads to anaerobic metabolism, where glucose is broken down without the presence of oxygen, producing energy in the form of adenosine triphosphate (ATP). This anaerobic energy production creates a rapid and powerful energy source, enabling you to perform high-intensity movements for short durations.
Elevated Heart Rate
HIIT involves short bursts of all-out effort, which significantly elevates your heart rate. This cardiovascular response is essential for optimizing oxygen delivery to muscles, removing waste products, and enhancing overall heart health. The rapid increase in heart rate during high-intensity intervals challenges the cardiovascular system and improves its efficiency over time.
Excess Post-Exercise Oxygen Consumptio
One of the most intriguing aspects of HIIT is the phenomenon known as excess post-exercise oxygen consumption (EPOC) or the “afterburn effect.” After a HIIT session, your body continues to require oxygen at an elevated rate to restore depleted ATP, replenish oxygen stores, clear lactic acid, and repair muscle tissues. This increased oxygen consumption results in additional calorie expenditure and fat oxidation, even during the recovery period, contributing to overall calorie burn and weight loss.
Elevation of Growth Hormones
HIIT has been shown to trigger the release of growth hormone and other signaling molecules that promote muscle growth, fat metabolism, and overall metabolic health. These hormonal responses contribute to muscle repair and adaptation, which are crucial for building strength and endurance.
Mitochondrial Biogenesis
Mitochondria are the powerhouses of cells, responsible for generating energy. HIIT has been linked to an increase in mitochondrial biogenesis, which involves the creation of new mitochondria within muscle cells. This enhances the cell’s ability to produce energy, ultimately improving endurance and exercise performance.
Enhanced VO2 Max
VO2 max, or maximal oxygen consumption, is a key indicator of cardiovascular fitness. HIIT has been shown to improve VO2 max significantly, indicating better oxygen utilization by the body. This improvement in oxygen transport and utilization contributes to enhanced endurance and overall athletic performance.
hiit benefits
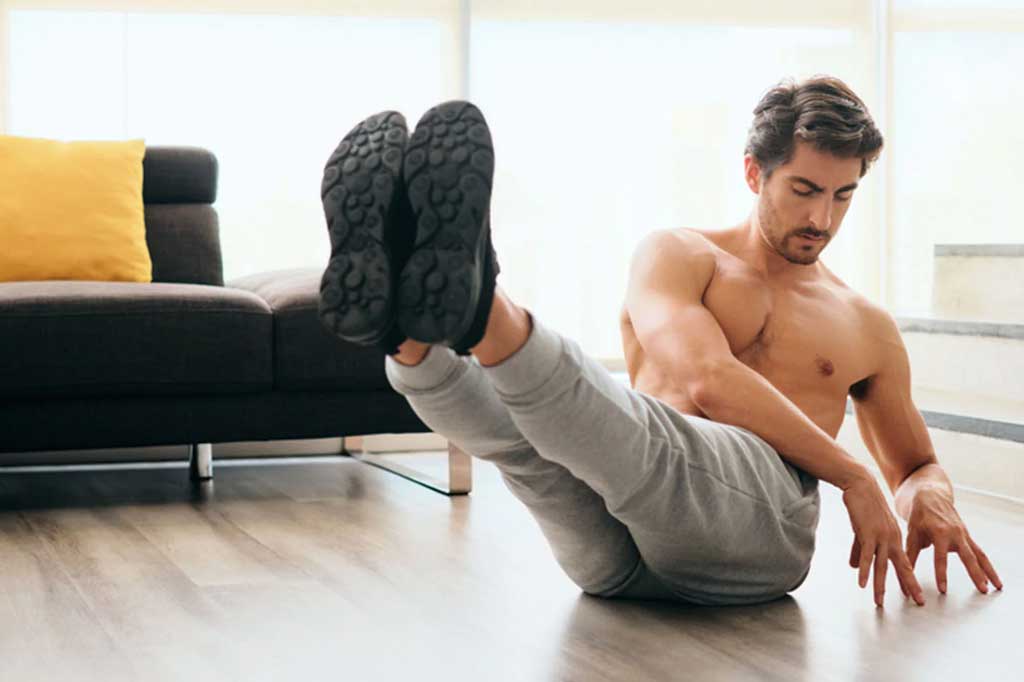

High-Intensity Interval Training (HIIT workout) has garnered immense popularity in the fitness world, and for good reason. This dynamic and time-efficient workout approach offers a plethora of benefits that cater to various fitness goals and lifestyles. Let’s unveil the remarkable benefits that HIIT brings to the table:
Efficient Calorie Burn and Fat Loss
HIIT is a potent tool for those aiming to shed extra pounds. The intense bursts of activity followed by short recovery periods lead to a substantial increase in calorie burn during the workout. Moreover, the afterburn effect or excess post-exercise oxygen consumption (EPOC) ensures that your body continues to burn calories at an elevated rate even after the workout has ended. This combination of calorie burn and EPOC contributes to effective fat loss and weight management.
Cardiovascular Health and Endurance
HIIT challenges your cardiovascular system by rapidly elevating your heart rate during high-intensity intervals. This leads to improvements in heart health, increased stroke volume (the amount of blood pumped per heartbeat), and enhanced oxygen delivery to muscles. Over time, HIIT can boost your overall endurance and aerobic capacity, allowing you to perform daily activities with greater ease.
Muscle Building
Contrary to the misconception that HIIT is only for cardio, it also has significant muscle-building benefits. The explosive movements and maximal efforts engage a variety of muscle fibers, leading to muscle development and increased strength. HIIT can help you achieve a toned and defined physique, especially when combined with resistance exercises.
Improved Insulin Sensitivity
HIIT has been shown to enhance insulin sensitivity, making your body more efficient at utilizing glucose for energy. This can contribute to better blood sugar regulation and reduce the risk of type 2 diabetes.
best hiit workout for beginners
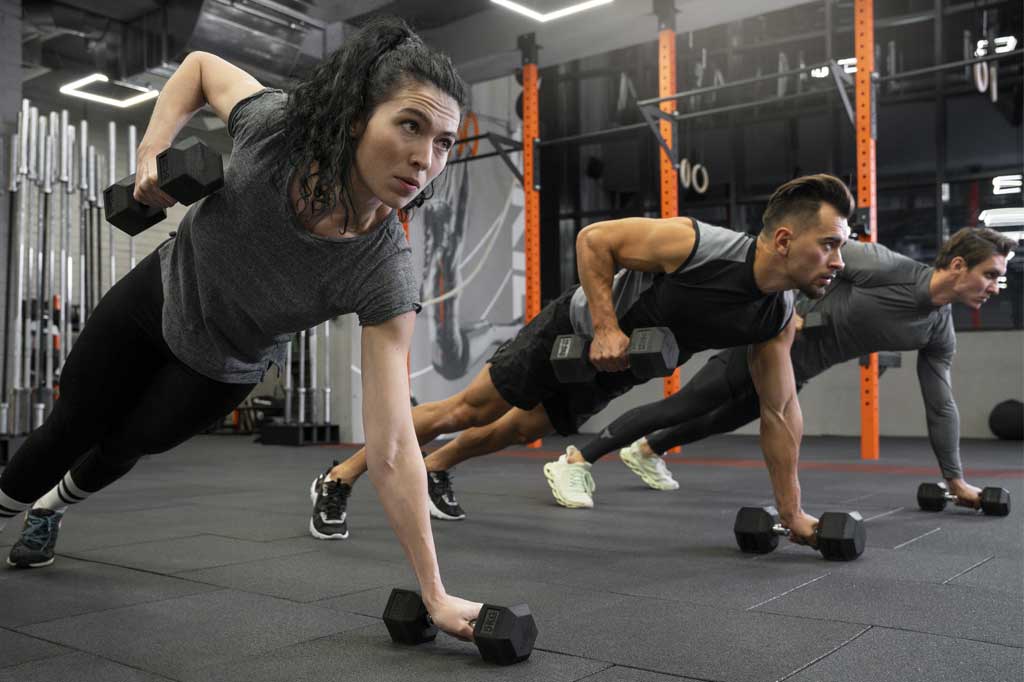

The “best” HIIT routine can vary depending on your fitness level, goals, and preferences. However, I can provide you with a sample HIIT routine that you can use as a starting point. Remember to adjust the intensity, work-rest ratios, and exercises based on your individual needs and capabilities. If you’re new to exercise or have any health concerns, it’s advisable to consult a healthcare professional before starting a new workout routine.
hiit workout Routine: Total-Body Blast
Duration: 20 minutes (including warm-up and cool-down)
Warm-Up: 3-5 minutes of dynamic stretching (e.g., arm circles, leg swings, hip rotations) followed by 2-3 minutes of light cardio (e.g., jogging in place, jumping jacks).
Work-Rest Ratio: 30 seconds of high-intensity exercise followed by 30 seconds of rest (modify as needed).
Exercises: Perform each exercise at maximum effort during the work interval, followed by 30 seconds of rest before moving on to the next exercise. Complete all exercises for one round, rest for 1-2 minutes, and then repeat for a total of 3-4 rounds.
- Burpees: Explosively jump up, go down into a push-up position, perform a push-up, jump back to a squat, and then jump up again.
- Mountain Climbers: Start in a plank position and alternate bringing your knees towards your chest in a running motion.
- Squat Jumps: Perform a squat, then explode up into a jump. Land softly and go back into a squat.
- High Knees: Run in place while bringing your knees up towards your chest as high as possible.
- Push-Ups: Perform push-ups with proper form, modifying on your knees if needed.
- Jumping Lunges: Start in a lunge position and jump to switch legs in mid-air, landing in a lunge on the opposite side.
- Plank Jacks: Start in a plank position and jump your feet out and in like a jumping jack motion.
Cool-Down: 3-5 minutes of static stretching (e.g., hamstring stretch, quad stretch, calf stretch) followed by deep breathing to gradually lower your heart rate.
Remember, this is just one example of a HIIT routine, and there are countless variations you can explore. You can mix and match exercises, adjust the work-to-rest ratios, and incorporate different movements to keep your routine challenging and engaging. As you progress, you can increase the duration of the workout or the number of rounds.
Always prioritize proper form and listen to your body. If an exercise feels too intense or causes discomfort, modify it or choose an alternative. Consistency is key, so aim to incorporate HIIT workouts into your routine 2-3 times per week, allowing sufficient time for recovery between sessions.
Conclusion:
Incorporating High-Intensity Interval Training (HIIT workout) into your fitness regimen can be a game-changer, offering a time-efficient and effective way to achieve a wide range of health and fitness goals. From torching calories and building lean muscle to boosting cardiovascular endurance and enhancing overall metabolism, the science-backed benefits of HIIT are hard to ignore. However, remember that safety and gradual progression are key to a successful HIIT journey. Before diving into the intensity, consult a healthcare professional, and always prioritize proper warm-up, technique, and recovery.
Take Action: Join Our Newsletter!
Ready to take your fitness journey to the next level? Stay updated with the latest insights, expert tips, and exclusive HIIT workout routines by subscribing to our newsletter. Whether you’re a seasoned athlete or just starting on your fitness path, our newsletter is your gateway to unlocking the full potential of HIIT and achieving your wellness aspirations. Sign up now and embark on a journey of transformation and vitality!









